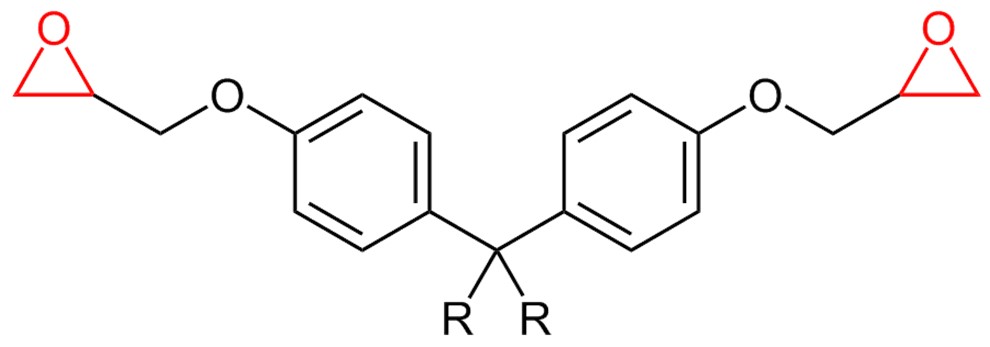
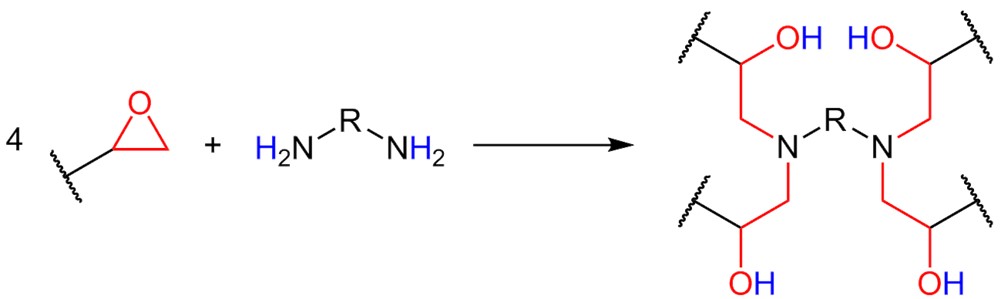
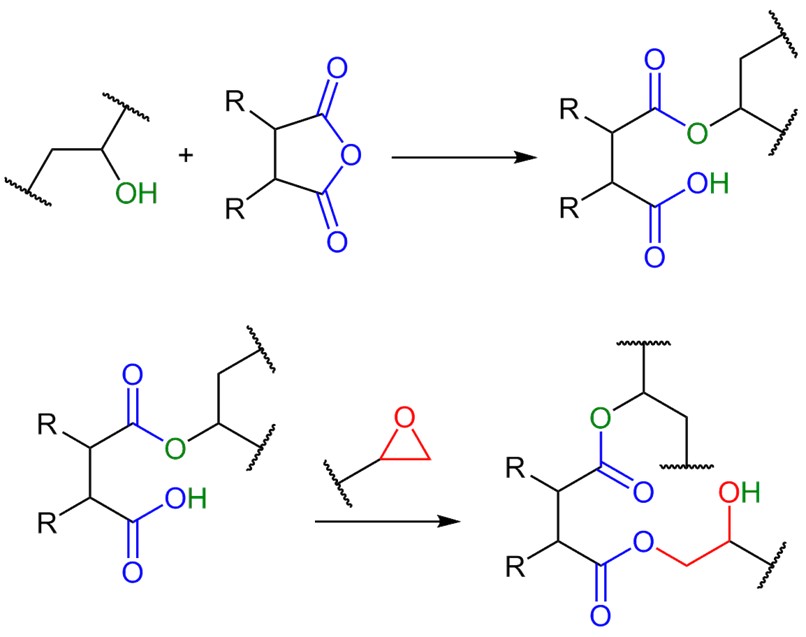
Epoxies are an important class of electronic casting resins. Classic applications include the encapsulation of motors, coils, electronic components, solid-state transformers and long rod insulators in high-voltage cable construction.
When cured, epoxy casting resins are characterized by high glass transition temperatures, good mechanical stability, good electrical properties and excellent chemical resistance. The extreme hardness of epoxies can lead to mechanical and thermal stresses, which are often accompanied by a certain degree of brittleness. The basic brittleness can be reduced by a suitable formulation, but usually cannot be completely avoided.
During processing (usually as a 2-component system), a distinction is made between cold-curing and hot-curing systems. Numerous properties of the epoxies can be specifically influenced by the use of various additives, fillers and other aggregates. The choice of hardener and the curing conditions are particularly important for the desired characteristics.